Search results
Author(s):
Jakub Podolec
,
Lukasz Niewiara
Added:
3 years ago
Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of coronary artery disease morbidity and mortality worldwide.1 Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)- lowering therapies have already become one of the most important in the prevention of atherosclerosis complications.2 Evolocumab is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) and thus significantly…
View more
Author(s):
Jeffrey Weitz
Added:
2 years ago
Dr Jeffrey Weitz (Thrombosis & Atherosclerosis Research Institute, Ontario, CA) presents the results of the Axiomatic-TKR Study, a phase II dose-ranging study that aims to examine the effect of Milvexian versus Enoxaparin in the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing total-knee replacement surgery.The study met its efficacy criteria, where the rate of thromboembolism was…
View more
Author(s):
Evan A Stein
Added:
3 years ago
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), discovered in 2003, is a circulating protein produced predominantly in the liver that plays a significant role in the recycling of LDL receptors (LDLRs).1,2 The LDLR, which normally recycles about 100 times in its lifetime, is the primary pathway for LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) clearance from circulation. Plasma PCSK9 binds to LDLRs along with…
View more
Author(s):
Nico A Blom
Added:
3 years ago
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) using biventricular pacing has been proven to be effective in adult patients with left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction and QRS prolongation. In this group of patients, CRT improves exercise tolerance, symptoms of heart failure and all-cause mortality.1 In addition, there is growing evidence that inter- and intra-ventricular dyssynchrony induced by…
View more
Author(s):
Alan S Maisel
Added:
3 years ago
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and congestive heart failure (CHF) are significant health risks affecting a large part of the population. In both diseases, early detection and initiation of treatment significantly reduce the risk of serious adverse events and death. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) have both shown considerable utility in the early diagnosis of patients…
View more
Author(s):
Marc P Allard-Ratick
,
Pratik Sandesara
,
Arshed A Quyyumi
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Historically, HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) has been inversely associated with adfverse cardiovascular outcomes such as MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.1–3 This led to widespread belief that HDL-C, in addition to LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), was a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
However, efforts to increase HDL-C in high-risk patients with well-controlled LDL-C values have not…
View more
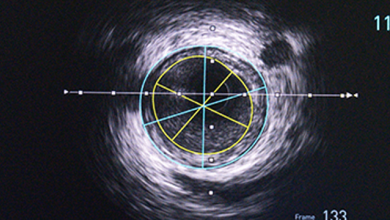
Role of IVUS in Complex PCI
Author(s):
Brandon Quintana
,
Akram Ibrahim
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Haytham Mously
,
Nischay Shah
,
Zachary Zuzek
,
et al
Added:
2 years ago
Author(s):
William T Abraham
Added:
3 years ago
Hyponatremia is the most common electrolytic abnormality in clinical practice and has a reported incidence of 15–30% in adults.1,2 It is particularly common in heart failure: the Organized Program to Initiate Life Saving Treatment in Patients Hospitalized for Heart Failure (OPTIMIZE-HF) registry recorded that 25.3% of 47,647 heart failure patients had hyponatremia on admission.3 In this registry,…
View more
Author(s):
Steven V Manoukian
,
Michele D Voeltz
,
Frederick Feit
Added:
3 years ago
Non-ST-segment elevation (NSTE) acute coronary syndromes (ACS) include unstable angina (UA) and NSTE myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and account for one and a half million hospitalisations in the US annually. Patients with ACS are typically managed by initial medical stabilisation followed by an early invasive approach, whereby cardiac catheterisation is performed, usually within 24 hours of…
View more











 « First
« First