Search results
Author(s):
Larry A Allen
,
John S Rumsfeld
Added:
3 years ago
Hospital readmissions contribute significant clinical and economic burden to patients and payers.1 Nearly 20 % of Medicare patients are readmitted to the hospital within 30 days of discharge, with heart failure listed as the most common reason for readmission.2 Based on a more than twofold variation in institutional readmission rates adjusted for patient clinical characteristics,3 preventable…
View more
Author(s):
Neal W White Jr
Added:
3 years ago
Hospital to Home (H2H) is a national quality improvement initiative of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI). It builds on the success of the ACC Door-to-Balloon Alliance for Quality and the IHI 100K Lives and 5 Million Lives campaigns. The goal of the H2H initiative is to reduce 30-day all-cause readmission rates for patients discharged with…
View more
Author(s):
Jesús Álvarez-García
Added:
7 months ago
ESC 23 — Dr Jesus Alvarez-Garcia (Ramon and Cajal University Hospital, ES) considers the use of ReDS technology in patients with acute heart failure (ReDS-SAFE HF) (NCT04305717) in this short interview.
The ReDS-SAFE HF study (Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai) aimed to test the remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) system, a novel electromagnetic technology that can noninvasively quantify…
View more
Author(s):
Miho Fukui
,
João L Cavalcante
Added:
3 years ago
Degenerative calcific aortic stenosis (AS) is one of the most common valvular heart diseases, affecting >3% of those aged >65 years in the West.1 As a result of an aging population, the prevalence of AS is expected to increase. Severe AS causes chronic pressure overload of the left ventricle (LV), resulting in LV hypertrophy (LVH), diastolic dysfunction, an increase in the size of the left…
View more
Author(s):
Alexandre Mebazaa
,
Harriette Van Spall
Added:
1 year ago
AHA 22 - Late-breaker host Dr Harriette Van Spall (McMaster University, CA) is joined by Prof Alexandre Mebazaa (University Hospitals Saint Louis‐Lariboisière, FR), the primary investigator of the anticipated STRONG-HF Trial (NCT03412201).
This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of rapid-optimization heart failuretherapies. 1800 patients were randomized to receive either usual care…
View more
Author(s):
Mitchell T Saltzberg
Added:
3 years ago
Volume Overload in Heart Failure
The burden of heart failure (HF) remains formidable in the US, with nearly one million annual hospital admissions and frequent outpatient visits to a variety of care providers.1 While HF outcomes have improved modestly over the past several decades, many patients still struggle to maintain a satisfactory quality of life.2 Implantable cardioverter–defibrillators…
View more
ESC 23: COP-AF Trial
Author(s):
David Conen
Added:
7 months ago
Video
Author(s):
Peter A McCullough
Added:
3 years ago
Heart failure (HF) is a common condition and carries a considerable age-dependent all-cause mortality. As a leading cause of hospitalization in adults, ~50% of patients discharged with a diagnosis of HF are readmitted within six months, and the one-year mortality rate is 20% after an initial diagnosis is established. There is currently a chronic HF epidemic with a rapidly expanding prevalence…
View more
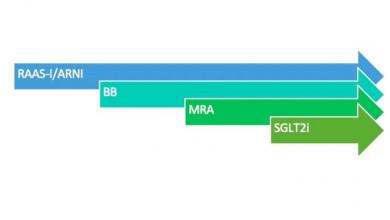
Author(s):
Neal M Dixit
,
Shivani Shah
,
Boback Ziaeian
,
et al
Added:
2 years ago
Author(s):
Mathew S Maurer
Added:
3 years ago
Cardiac output (CO) is a fundamental measure for the assessment of cardiac performance and is applied widely to detect the presence of cardiovascular disease and monitor its progression, as well as to monitor patients in challenging hemodynamic circumstances and to optimize therapy. CO is a key parameter in characterizing a patient’s hemodynamic state. For example, a notable characteristic of…
View more